Fever Blisters & Canker Sores
Overview
Both fever blisters and canker sores are common across all ages and can be painful. However, they are separate conditions with different causes. Read further to learn how to tell them apart and find out which treatments might help ease the pain.
Fever Blisters (also known as cold sores) are painful fluid-filled sores that form on the outside of the mouth around the lips. Fever blisters are very contagious.
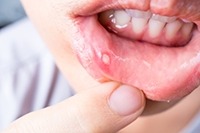
Canker Sores are painful white or yellow sores that only form inside the mouth, usually on the insides of the cheeks or lips or on the tongue. Canker sores (also called aphthous ulcers) are not contagious.
Causes
Fever Blisters are caused by an infection with the herpes simplex virus, usually type 1, or HSV-1. It is estimated that nearly 90 percent of U.S. adults have been infected with the virus, although many people with the infection do not ever show symptoms. The virus generally resides in the nerve cells where it may periodically reactivate, traveling to the skin and causing recurring fever blisters.
Canker Sores do not have a known cause. They may be triggered by an injury, stress, smoking, or deficiencies in folic acid, iron, or vitamin B12.
Symptoms
Symptoms of fever blisters:
- Fluid-filled blisters on the outside of the mouth around the lips.
- Burning or tingling sensation at the site where the blisters will appear.
- And sometimes, fever, fatigue, or swelling of the lymph nodes, similar to other viral infections.
Symptoms of canker sores:
- A round white or yellow sore with a red border inside the mouth, usually on the inside of the lips or cheeks or on the tongue.
- A burning or tingling sensation may occur in the mouth prior to the formation of the sore.
Diagnosis
The main way to tell the difference between a fever blister and a canker sore is by location. Fever blisters occur outside the mouth, generally around the border of the lips. Canker sores occur inside the mouth.
They also differ in appearance: Fever blisters are patches of several small fluid-filled blisters, while canker sores are usually single round white or yellow sores with a red border.
| Fever Blisters vs. Canker Sores | Fever Blisters | Canker Sores |
|---|---|---|
| Location: | On the outside of the mouth around the lips | Inside the mouth |
| Appearance: | Collection of small, fluid-filled blisters | Usually a single round white or yellow sore with a red border |
| Cause: | An infection with the herpes simplex virus type 1, or HSV-1 | Unknown |
| Contagious? | Yes | No |
Treatment
Typically, both types of sores go away on their own and treatment is not usually required. There is no known treatment that can permanently cure fever blisters or canker sores and prevent them from recurring. Treatment focuses on minimizing the pain and speeding recovery time.
Fever blisters can be treated with prescription antiviral medications either applied as topical creams or taken orally. See a doctor if your cold sores persist longer than a few weeks, you develop a high fever, or you notice eye irritation.
Canker Sores can be treated with over-the-counter (non-prescription) gels to numb the pain. Avoiding spicy or abrasive foods may also help. Rinsing the mouth with over-the-counter antiseptic medications may help prevent infection of the sore and speed healing.
See a doctor if you have frequently recurring canker sores or if the sores are severe enough to make eating or drinking difficult. If you have recurring canker sores as a result of a vitamin deficiency, treating the deficiency may reduce their frequency.
Helpful Tips
Both fever blisters and canker sores can have triggers that produce flare ups. Try to identify and then avoid triggers so your flare ups become less frequent.
Tips for Fever Blisters
- Sun exposure may sometimes trigger outbreaks of fever blisters. If you have recurring blisters, using sunscreen may help reduce their frequency.
- Fever blisters are contagious. Avoid kissing, sharing eating utensils, cups, water bottles, or other items if you are experiencing symptoms.
- Be aware that in young children, fever blisters can cause loss of appetite, drooling, and fever that can last for several days.
- Talk to your doctor or your child’s pediatrician if symptoms are severe or recur frequently.
Tips for Canker Sores
- If you regularly get canker sores, talk to your doctor about testing for food allergies, as allergic reactions can sometimes trigger canker sore outbreaks.
Additional Resources
- MedlinePlus (Fever Blisters)
Information about oral herpes (the infection that causes cold sores) from the NIH National Library of Medicine. - MedlinePlus (Canker Sores)
Information about canker sores from the NIH National Library of Medicine.
December 2024